

- Home
- Companies
- Bioconservacion SA
- Articles
- Project - Emergency Equipment for ...
Project - Emergency Equipment for Chlorine Adsorption in Hospitals
Chlorine is a strong oxidant that under normal conditions and in its pure state forms dichlorine, a yellow-greenish toxic gas formed by diatomic molecules (Cl2) about 2.5 times heavier than air, with an unpleasant and toxic odor.
Among its many applications and due to its strong oxidizing character, it stands out especially for being a compound widely used in water purification in WWTPs (wastewater treatment plants) and as a disinfectant in other applications.
In WWTPs, instead of treating water directly with chlorine gas, hypochlorite solutions are used, which gradually release chlorine into the water and are capable of eliminating bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. However, in other sectors such as hospitals, chlorine is usually stored in liquefied gas cylinders where a leak could generate dangerous environments and are therefore confined in containment rooms with safety systems. The disadvantage of using chlorine in this format lies in the necessary storage and transport conditions. The high toxicity of the gas, which causes damage at levels of 0.1 ppm in the air, makes it necessary to handle this product only with special equipment, with rescue and contingency programs duly established by trained personnel.

Main Chlorine elimination technologies; pros and cons:
Among the most common chlorine removal systems are adsorbents (dry media) and chemical scrubbers (wet scrubbers).
Classical adsorbents have several advantages over chemical scrubbers, chemical scrubbers require significantly more intensive maintenance than adsorbents. The instrumentation of scrubbers, consisting of pumps, nozzles and valves, is more complex. All this leads to greater risks in terms of operation.
Another aspect that penalizes chemical scrubbers is directly related to the use of caustic liquids that generate a liquid effluent that requires post-treatment. Adsorbents, on the other hand, eliminate the contaminant permanently, transforming it into harmless substances. Depending on the operating conditions, the spent adsorbent can even be used as fertilizer.
Finally, another great advantage of adsorbents over chemical scrubbers is the fact that they are a solution capable of maintaining efficiencies above 99.9% regardless of the load fed to the reactor.
All these advantages are leading the market to choose adsorbents as a more effective solution, both technically and economically, over chemical scrubbers.
Bioconservacion has developed a specific filter media to eliminate chlorine and acid vapors. BION Clear is a clay impregnated with sodium thiosulfate capable of achieving chlorine removal capacities of up to 9% w/w.
The reaction mechanism of BION Clear removes chlorine through the processes of adsorption, absorption and chemisorption. The chlorine is transformed into harmless solid substances that are irreversibly trapped in the pellet.
This media is specially designed for use in applications where significant concentrations of chlorine may be released such as the pulp and paper manufacturing industry, wastewater/urban disinfection or fumes from laser cutting PVC.
In 2013, BION, together with its distributor in Peru, Requinor, carried out a project consisting of the implementation of a chlorine safety equipment in a hospital in Peru
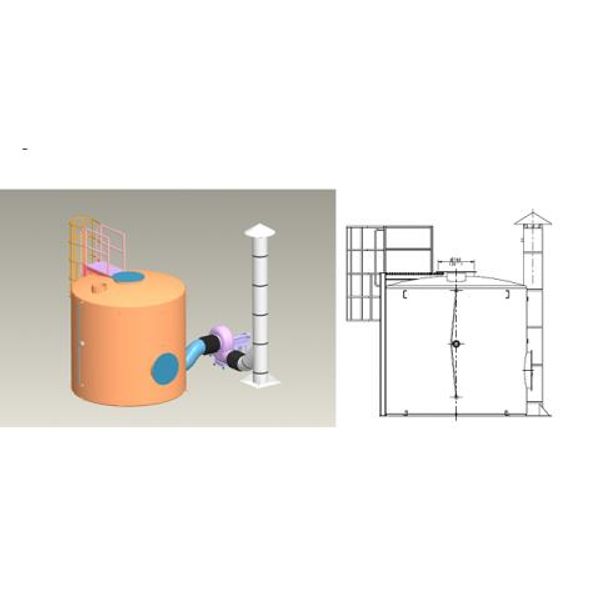
In this hospital, the chlorine cylinders are confined in a room of a certain volume and, following the American standard Uniform Fire Code Article 63 (NFPA 1, 2006), an equipment packaged with BiON Clear was designed.
Depending on the standard followed in the design of the safety system, the equipment will have different dimensions. The conceptual basis of the standard is to design equipment capable of adsorbing a volume of chlorine gas emitted by a rupture in a chlorine cylinder. In this way, the safety system must be capable of aspirating a certain flow of gas to produce a depression in the room and be efficient in adsorbing the chlorine.
Bioconservacion designed equipment with the following characteristics:
- Reactor made of fiberglass reinforced polyester.
- Klopper-shaped roof.
- Access railing.
- Reactor height: 2950 mm.
- Outer diameter: 1500 mm.
With this equipment it was possible to ensure a chlorine removal efficiency of more than 99.9%, ensuring an output below 50 ppbv at all times.
In addition to the reactor with the chemical media, Bioconservacion/Requinor designed the piping and the high-pressure centrifugal fan for the safety system.
As is customary in our company, there continues to be collaboration with Requinor in terms of data exchange, advice, incident resolution, etc., which allows us to strengthen ties and work together on future projects.
