- Primary Cells - Human - Cell Systems - Adipose Cell System
- Primary Cells - Human - Cell Systems - Cardiac Cell System
- Primary Cells - Human - Cell Types - Adrenal Cortical Cells
- Primary Cells - Human - Cell Types - Endothelial Cells
- Cell Culture Media
- Stem Cells - Human Pluripotent Stem Cells - Medium and Reagents
- Genetics & Genomics - qPCR Array Kits - Body Systems - General Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology - RNA
ScienCell Research Laboratories products
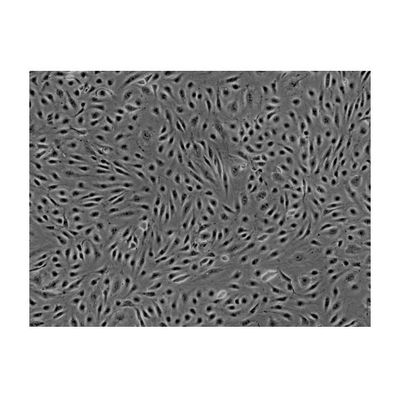
Primary Cells - Human - Cell Systems - Adipose Cell System
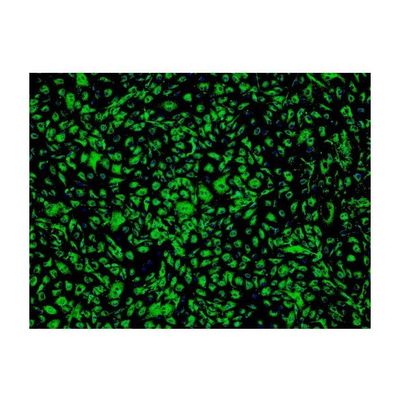
ScienCell - Model HAMEC 7200 - Human Adipose Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Microvascular endothelial cells line blood vessels and contribute to many biological processes such as angiogenesis, coagulation, trafficking of lymphocytes, and the inflammatory response. Microvascular endothelial cells are diverse and have specific cellular characteristics and functions depending on the organ/tissue in which they are located. Adipose tissue is unique because it has the capacity to continually grow throughout adult life. Thus, it has a high level of angiogenesis to provide the extensive vascularization required for adipose tissue. Studies have shown that angiogenesis precedes adipogenesis, implying that microvascular endothelial cells influence the proliferation of preadipocytes. At the same time, microvascular endothelial cell growth is stimulated by adipocyte secreted VEGG, suggesting a complex paracrine relationship between microvascular endothelial cells and preadipocytes during tissue development.
Primary Cells - Human - Cell Systems - Cardiac Cell System
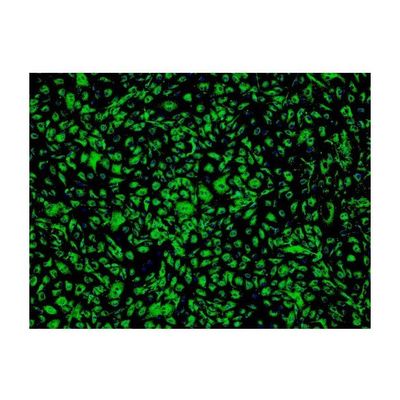
ScienCell - Model 6000 - Human Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMEC) play important roles in myocardial function. CMEC regulate vascular tone by releasing and degrading endothelium-derived vasoactive factors, and modulating the local levels of vasoconstrictors and vasodilators through their enzymatic activities. Many of these substances can also modify myocardial contractile behavior. Furthermore, microvasculature has been shown to participate in the regulation of leukocyte recruitment, inflammation, and angiogenesis. They are also capable of trans-differentiating into myofibroblasts, suggesting a role in aberrant accumulation of matrix and fibrotic disorders. CMEC cultures provide an invaluable tool for understanding CMEC physiological and pathophysiological relevance in cardiac function and disease.
Primary Cells - Human - Cell Types - Adrenal Cortical Cells
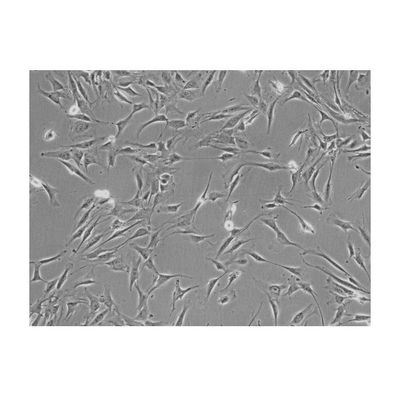
ScienCell - Model 3610 - Human Adrenal Cortical Cells
The adrenal cortex makes up the perimeter of the adrenal gland and plays an essential role in regulating homeostasis in the body through the secretion of corticosteroid and androgen hormones. The secreted steroids arise from the three zones that form the adrenal gland and these zones provide the framework for the adrenal cortex. The cells in the cortex stem from the mesoderm and form three concentric zones: the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculate, and zona reticularis. Studies have shown that there is extensive interaction between the cortical and medulla regions of the adrenal gland, with cortical cells located within the adrenal medulla and chromaffin cells located within the adrenal cortex. The close contact of these two cell types implies intercellular exchange and allows for further studies of paracrine signaling between the two adrenal endocrine systems. Adrenal cortical cells can be used for further research of hormonal regulation and steroidogenesis.
Primary Cells - Human - Cell Types - Endothelial Cells
ScienCell - Model 1000 - Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMEC), the major component of the blood-brain barrier, limit the passage of soluble and cellular substances from the blood into the brain. BMEC have unique features to distinguish themselves from those of peripheral endothelial cells, such as 1) intercellular tight junctions that display high electrical resistance and slow paracellular flux, 2) the absence of fenestrae and a reduced level of pinocytic activity, and 3) asymmetricallylocalized enzymes and carrier-mediated transport systems. Similar to peripheral endothelial cells, BMEC express, or can be induced to express, cell adhesion molecules on their surface that regulate the extravasation of leukocytes into the brain. BMEC have been widely used for studying the molecular and cellular properties of blood-brain barrier because of their unique functions.
Cell Culture Media
ScienCell - Model 7501 - Mesenchymal Stem Cell Medium
Stem Cells - Human Pluripotent Stem Cells - Medium and Reagents
StemCryo - Model 0163 - Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cryopreservation Medium (5 x 10 ml)
StemCryo® is a sterile, uniquely formulated medium designed for the cryopreservation of human pluripotent stem cells (e.g. human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells). This fully defined, animal-component free, serum-free medium provides optimal cell recovery efficiency while maintaining cell pluripotency. This product has a pH of 7.2 at room temperature.
Genetics & Genomics - qPCR Array Kits - Body Systems - General Cell Biology
GeneQuery - Model GK056 - Human Hemostasis qPCR Array Kit
ScienCell’s GeneQuery™ Human Hemostasis qPCR Array Kit (GQH-HEM) profiles 88 key genes involved in stopping bleeding. Upon wounding, hemostasis generally involves vasoconstriction to prevent blood flow to the afflicted area, forming a temporary plug to inhibit bleeding, and then coagulation or blood clotting. Examples of disorders in hemostasis are hemophilia, thrombosis, and embolisms.
Molecular Biology - RNA
ScienCell - Model 1837 - Human Astrocytes-hippocampal MicroRNA
Human Astrocyte-hippocampal microRNA (HA-h miRNA) is prepared from early passage Human Astrocytes-hippocampal using Life Technologies’ mirVanaTM miRNA Isolation Kit. The microRNA is purified by organic extraction and enriched by immobilization of RNA on glass-fiber filters. The microRNA is eluted and stored in nuclease-free water. MicroRNA from ScienCell Research Laboratories is a convenient and cost effective alternative to acquiring expensive tissues.