- Home
- Companies
- Senzime AB Uppsala
- Services
Senzime AB Uppsala services
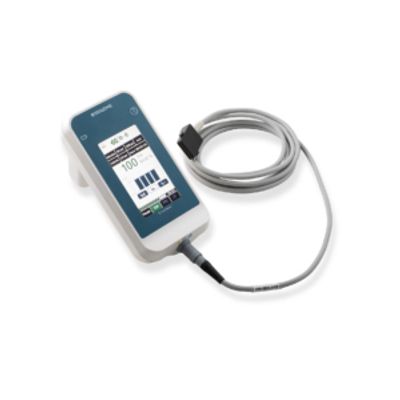
NMT Monitoring Services
Qualitative vs Quantitative NMT Monitoring Services
Qualitative vs quantitative NMT monitoring- the neuromuscular assessment can be subjective or objective. Visual or tactile assessment of the twitch responses is considered qualitative (subjective) neuromuscular assessment, because the clinician guesses the degree of fade or recovery, instead of measuring the strength of responses. The result is therefore subjective and unreliable, regardless of the clinician’s level of experience or training. Low, but still clinically meaningful degrees of neuromuscular blockade can only be measured using a quantitative, objective, monitoring device. A residual neuromuscular block of TOFR > 0.4 cannot be reliably detected by tactile or visual means even by an experienced clinician. Clinical tests, such as 5-s head-lift, tidal volume, grip strength or 5-s leg lift do not guarantee complete resolution of neuromuscular block and should not be used to make clinical decisions about the adequacy of neuromuscular function.
EMG – The new Gold Standard in NMT Monitoring Services
Like other technologies, EMG involves stimulation of a peripheral nerve and measurement of the response that is generated by the contraction of the innervated muscle. The difference from other technologies is that EMG measures an electrical event that occurs at the neuromuscular junction; the activation of postsynaptic receptors by acetylcholine (a chemical process) that converts it to a mechanical response (excitation- contraction coupling), that results in muscle contraction. Because measurement of function does not depend on physical movement (as MMG, AMG or KMG require), EMG is a better indicator of pure neuromuscular function- EMG is the new gold standard.