The Electrospinning Company Ltd. products
Electrospinning - Biomaterials
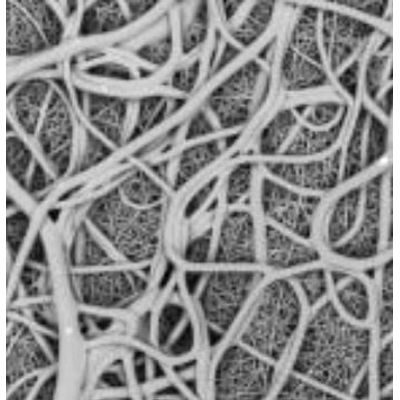
Electrospinning is an established method of producing nano- and micro-fibres from a wide variety of natural and synthetic polymers. A polymer solution is injected through a nozzle or needle which is charged to a high voltage. The applied voltage induces a charge on the surface of the liquid droplet and when this is sufficiently high, the hemispherical surface of the fluid elongates and a Taylor cone is established. On increasing the applied voltage further, a charged liquid jet is ejected from the Taylor cone and attracted to the earthed collector, which is positioned at a fixed distance from the needle. During this process the solvent evaporates from the polymer solution, leaving dry polymer fibres on the collector. Electrospinning with a single Taylor cone is typically low throughput but new equipment, such as multi-nozzle injectors and needle-less spinnerets, and processes are facilitating industrial scale-up.
3D Cell Culture
Electrospinning - Liver Cancer Cell
Images taken using a Nikon Eclispe C1 confocal microscope. HepG2 liver cells were grown for 21 days in the Mimetix scaffold. Cells are stained with DAPI and actin; fibres are electrospun together with Rhodamine 6G (a and b). Cancer cells form a 3D network inside the scaffold (c), use the fibres to support themselves (d) and populate the entire scaffold (e).
Electrospinning - Breast Cancer Cells
The Mimetix fibres are labelled with Rhodamine 6G. The thickness of Mimetix scaffold allows for having a 3D environment while maintaining a certain translucence, thus allowing for easy and robust imaging. This study has investigated the localisation depth of MCF7 breast cancer cells in the Mimetix scaffold after 4 days of culture (nuclei stained with TO-PRO-3, blue). The video below shows a Z-stack (slices through the scaffold from the top to the bottom at 2 μm steps), 4 days after seeding. At day 1 most cells are located with the top 1/3 of the scaffold, whereas they occupy the top 2/3 of the scaffold with few cells observed even deeper at day 4.
Materials
Electrospinning - Electrospun Biomaterials
The advantages of electrospinning are the ability to tailor polymer, architecture and structure to create nanofibre and microfibre materials suitable for different therapeutic applications.
Symatix - Synthetic Amniotic Membrane
The Electrospinning Company is developing the Symatix® membrane which is an innovative synthetic amniotic membrane substitute. The membrane is created using electrospinning technology and is designed to overcome the limitation of the Human Amniotic Membrane (HAM).