

- Home
- Companies
- CardioWise Inc.
- News
- CardioWise Stretch Quantifier for ...
CardioWise Stretch Quantifier for Endocardial Engraved Zones (SQuEEZ) Receives Patents from Both the United States and the European Union
CardioWise, Inc., is pleased to announce two significant patents protecting its heart function analysis software, Stretch Quantifier for Endocardial Engraved Zones (SQuEEZ). The European Union Patent Number 12839978.9 was awarded on February 2, 2019, followed closely by the U.S. Patent on June 7, 2019 (patent application number 14/350,991). Both patents are entitled “Methods for Evaluating Regional Cardiac Function and Dyssynchrony from a Dynamic Imaging Modality using Endocardial Motion,” and were awarded to The Johns Hopkins University (JHU) for its pioneering work on a mathematical software algorithm that utilizes cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) data to determine the regional contractile function of the heart muscle at high resolution. The research and development of SQuEEZ was completed by co-inventors, Dr. Elliot R. McVeigh and Dr. Amir Pourmorteza, who worked with their team at JHU sponsored by R01 research grants from the National Institutes of Health.
Dr. McVeigh is Professor of Biomedical Engineering at the University of California, San Diego and was formerly Chair of Biomedical Engineering at JHU. Dr. McVeigh is the co-Director of the Center for Translational Imaging and has a 30- year history of research in medical imaging, particularly cardiovascular CT and MRI. Dr. Amir Pourmorteza, PhD, is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences at Emory University School of Medicine. Dr. Pourmorteza is a biomedical engineer and CT physicist specializing in cardiovascular imaging, spectral computed tomography, tomographic reconstruction, and artificial intelligence in medical imaging. He obtained his PhD in Biomedical Engineering and completed a Fellowship in Tomographic Reconstruction from Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland where he was the co-inventor of SQuEEZ with Dr. McVeigh.
They and their team developed and validated clinical applications for the patented technology in eight peer-reviewed, scientific publications.
The patent is based on the ability in sequential high resolution to track points on the endocardium as they move during the contraction of the heart to allow quantitative assessment of regional myocardial heart wall motion. The analysis of four dimensional SQuEEZ parameters has the potential to improve the ability to quantify accurately the regional myocardial contractile function (ability of the heart to pump blood) through the heart muscle of the left ventricle. The key aspect of the invention is that the individual patient strain data are compared regionally within the left ventricle of the heart to a “normal” patient SQuEEZ database that was compiled by the inventors. Using this database information, each patient-specific SQuEEZ value at each of the points can be related to the normal data range within the normal patient database.
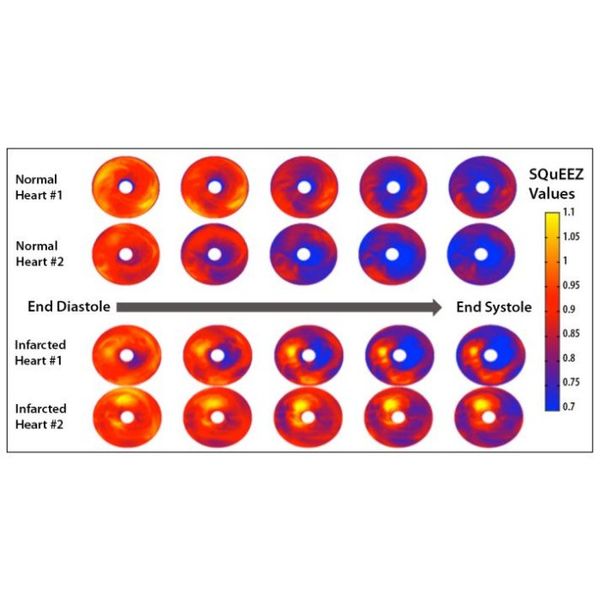
The image at the left displays the left ventricular SQuEEZ “bullseye” maps of two patients with normal hearts (top) and two patients with infarcted hearts indicating cardiovascular disease. The analysis clearly shows large abnormal yellow areas indicating areas of the endocardial wall that are not moving normally due to the damage.
Cardiac CT combined with SQuEEZ analysis software can provide clinicians with a normalized measurement to determine the answer to the first and most important clinical question that a cardiac surgeon needs to know for a patient who presents with cardiovascular disease symptoms—“Is the contractile function normal or not normal?” SQuEEZ allows the surgeon to make a more informed decision about the proper intervention for the patient, whether it is a drug, surgery or medical device, and then follow the patient’s recovery and progress after the procedure, non-invasively and with extremely low exposure to radiation. The software is an intuitive, quantitative method to classify LV contractile function that has the potential to provide significant improvement in clinical decision-making relative to the inconsistent, qualitative tests used today. The software provides the ability to both quantify and localize left ventricular (LV) contractile dysfunction. This will improve clinical outcomes by addressing limitations of the current nonquantitative metrics of regional LV function. The software creates an objective standard that increases accuracy by reducing the user variability that has plagued interpretation of LV functional analysis. The simplicity of interpreting and displaying these results will increase patients’ understanding of their coronary artery disease.
Another application for SQuEEZ is to evaluate the Right Ventricle, a chamber of the heart that is difficult to evaluate with other imaging modalities. Quantification of the motion of the right ventricular wall motion is important to evaluating patients with pulmonary hypertension, a fairly common heart problem.
Jack Coats, CEO of CardioWise, Inc. said, “We are very pleased that the patents for SQuEEZ have been awarded to Dr. McVeigh and Dr. Pourmorteza from their work at Johns Hopkins University. Their pioneering efforts over the past 10 years to develop the technology that has resulted in SQuEEZ have brought extremely important new quantitative metrics to evaluate and treat patients with cardiovascular disease. What makes SQuEEZ such a valuable tool to clinicians in the diagnosis of heart disease is the quantitative comparison of the individual patient data to the normal hearts database collected and compiled by Dr. McVeigh’s team. CardioWise then can make the SQuEEZ analysis available to caregivers and patients on any mobile device in an easy-to-read, quantitative 4D color model, allowing patients to participate in decisions about their care.”
CardioWise™ is commercializing patented, non-invasive Cardiac CT analysis software that produces a quantified 4D image model of the human heart, called Stretch Quantifier for Endocardial Engraved Zones™ (SQuEEZ™). CardioWise heart analysis software combined with cardiac CT is a single diagnostic test that is able to provide quantitative analysis of the myocardium, arteries and valves with an unprecedented level of detail. It has the opportunity to become the new gold standard of care for heart health analysis. CardioWise™ is a VIC Technology Venture Development™ portfolio company.
