

- Home
- Companies
- Piramal Critical Care (PCC)
- Products
- Piramal - Ampicillin and Sulbactam for ...
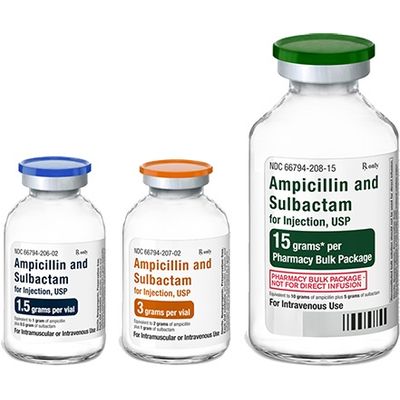
Piramal - Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP
Piramal`s Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is available through the wholesaler ordistributor of your choice
PRODUCT NAME AND COMPOSITION: Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, an injectable antibacterial combination consisting of the semi synthetic antibacterial Ampicillin sodium and the beta-lactamase inhibitor Sulbactam sodium for intravenous and intramuscular administration. Supplied in 1.5 grams vials (lgram Ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 gram Sulbactam as the sodium salt) and 3 grams vials (2 grams Ampicillin as the sodium salt plus lgram Sulbactam as the sodium salt).
Please referto Full Prescribing Information (FPI) before prescribing.
INDICATIONS: Treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed in the FPI.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: See FPI for full details. Ampicillin and Sulbactam for injection may be administered by either IVor IM routes. For intravenous administration, the dose can be given by slow intravenous injection over at least 10 to 15 minutes or can also be delivered in greater dilutions with 50 to 100 mLofa compatible diluent as an intravenous infusion over 15 to 30 minutes. Ampicillin and Sulbactam for injection may also be administered by deep intramuscular injection. The recommended adult dosage of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for injection is 1.5 grams (1 gram Ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 gram Sulbactam as the sodium salt) to 3 grams (2 grams Ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 gram Sulbactam as the sodium salt) every six hours. The total dose of Sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day. Pediatric Patients (1 year of age or older): The recommended daily dose is 300 mg per kg of body weight administered via intravenous infusion in equally divided doses every 6 hours. Pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or more should be dosed according to adult recommendations. Patients with Impaired Renal Function: The elimination kinetics of Ampicillin and Sulbactam are similarly affected, hence the ratio of one to the other will remain constant whatever the renal function. The dose of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for injection in such patients should be administered less frequently in accordance with the usual practice for Ampicillin.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: History of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to Ampicillin, Sulbactam or to other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs (e.g., penicillins and cephalosporins). History of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic dysfunction associated with Ampicillin and Sulbactam for injection.
COMMON SIDE EFFECTS: Local: Pain at IM injection site (16%), pain at IV injection site (3%), thrombophlebitis (3%), and phlebitis (1.2%). Systemic: Diarrhea (3%), rash (less then 2). See FPI for a complete list.
