HBOT - Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
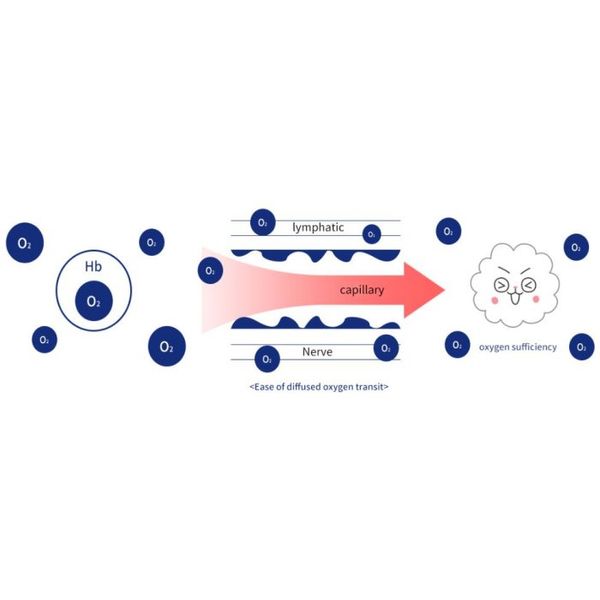
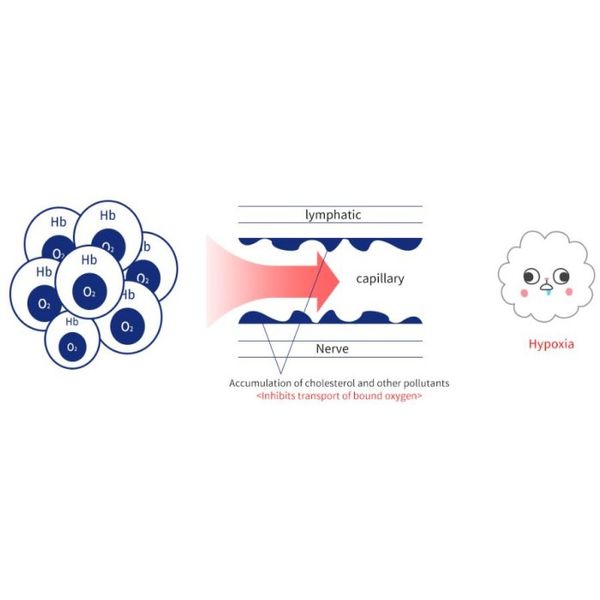
Bound oxygen vs. Dissolved oxygen: There are two types of oxygen in the body-oxygen which is bound to hemoglobin and oxygen which is dissolved freely in the blood. Normal respiraton only involves transport of oxygen which is bound to hemoglobin. However, because hemoglobin is larger than the size of most capillaries in such vital organs as the lungs, kidneys, liver, and skin, hemoglobin-bound oxygen transport is not sufficient to attain full-body blood circulation.
- Bound to hemoglobin in the blood.
- Cannot be transported in a greater amount than that of hemoglobin it self.
- Hemoglobin is a large molecule that has difficulty passing through capillary walls. (cannot pass through about 90% of capillaries in the body)
- About 99% of oxygen in the body is bound to hemoglobin.
- The body cannot get sufficient oxygen through normal respiration. (increased inhalation cannot solve this deficiency)
- Beause oxygen is a small molecule. if it is dissolved in the blood, it can easily pass through capillary walls.
- Abount of dissolved oxygen in the blood does not depend on amount of hemoglobin.
If the atmospheric pressure of oxygen is high, oxygen will not only readily bind with hemoglobin in red blood cells, the content of dissolved oxygen will be increased, transport across capillary walls will efficient, free movement into the smallest areas of the circulatory system will become easier, and cellular activity will also be increased.