

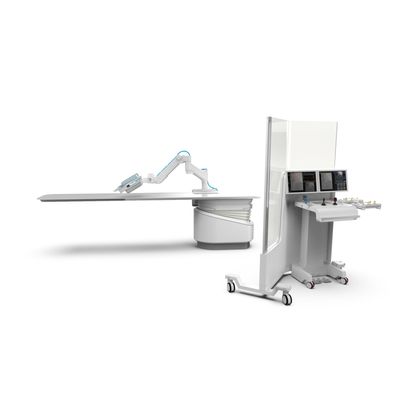
Robocath - Model R-One - Medical Robot
Innovation is at the heart of Robocath’s strategy, making R-One™ a unique solution, protected by over 60 international patents.
R-One™ robotic assistance platform was designed using a global approach to the needs of interventional cardiology. It integrates flawlessly with the interventional protocol. R-One™ is designed to provide physicians with reliable, precise assistance during procedures and enhance movements creating better interventional conditions, in particular by being totally protected from x-rays.
R-One™ comprises two core elements:
- Radio-protected control unit: a mobile radioprotection control station with a mobile radiation protection screen that protects medical staff from x-rays, and the command unit (joysticks). With this unit, the physician remotely controls instruments in the vascular system safely and accurately
- Robotic unit: comprising the robot and its articulated support arm
The architecture of medical robot R-One™ permit to use two guide/stent-balloon units can be used (non-simultaneously). It is compatible with market leading devices (guidewires, stent/balloons, imaging systems, etc.). It takes just a few minutes to install and integrates flawlessly with the intervention protocol, without adding any additional steps.
To get more information of R-One™, the user manual can be provided on request through the contact page and Safety information is available in the link below in the section "Safety Information".
The Robocath team is committed to provide physicians and their teams with the support they need to guarantee optimal use of our medical robot. R-One™ robotic platform is the result of years of scientific collaboration between highly experienced phyisicians and the Robocath engineers who developed R-One™. Consequently, this relationship is built on trust; ongoing communication is very important to us. We are committed to providing training, monitoring and ongoing support to guarantee the proficiency of the whole medical team in using our system.
Innovation is at the heart of Robocath’s strategy. New patents are regularly filed for new technologies that will be used in future medical specialties. Robocath’s aim is to guarantee the same access to treatment for all through the development of remote interventions, including the remote treatment of vascular emergencies such as strokes. This model will provide better care for this type of pathology, more quickly and under better conditions. Research is currently underway to develop robotics platforms for peripheral vascular and neurovascular procedures.
- Hypertension
- Lack of physical activity
- Abdominal obesity
- High cholesterol level
- Smoking
- Poor diet
- Psychosocial issues
- Diabetes
Establishments equipped with R-OneTM can position themselves as centers of excellence for interventional cardiology and attract top-level physicians.
Equal access to care
In the long term, remote treatment of vascular emergencies (from an expert hospital center to another situated elsewhere) will mean all patients can be offered the best treatment as soon as possible.
A stroke can manifest as partial or total paralysis of one or more limbs, reduced feeling or numbness affecting the face, speech difficulty (incoherent speech), balance and memory issues, and vision problems.
What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease is caused by a narrowing of the coronary arteries due to a build-up of calcified deposits, or plaque, on the vessel walls. This process is called atherosclerosis.
Two main arteries supply blood to the heart – the left coronary artery (which in turn splits into two smaller arteries, the left anterior descending and the left circumflex artery), and the right coronary artery. These arteries are the main blood vessels that ensure the heart muscle gets enough oxygen. There is little communication between the two. As a result, the occlusion (blocking) of these vessels rapidly causes necrosis (tissue death) of the heart muscle. This is called myocardial infarction.
Myocardial infarction is the leading cause of death worldwide.
Time is a significant variable in treating coronary artery disease.
A number of factors increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease:
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes (elevated blood sugar)
- Cholesterol: an elevated level of fats, particularly LDL cholesterol, in the blood is a major risk factor. Low HDL cholesterol is also a risk factor.
- Being overweight
- Lack of physical activity
As coronary artery disease develops slowly, symptoms appear at a late stage, when the narrowing has already reached a certain level.
One of the first symptoms is a feeling of ‘tightness’ in the chest on exertion (walking quickly, running, etc.), called angina. This takes the form of intense pain deep in the chest, and is a sign that the heart muscle is not getting enough oxygen.
It may also be felt after meals, when digesting food, or when resting at night. Often, it feels like this pain is radiating into the left arm. It can also radiate into the neck, the lower jaw, the right arm, or into the back and stomach.
This intervention is carried out following a coronary angiogram, which determines the area to be treated and the degree of stenosis requiring revascularization.
The R-OneTM robotic platform was designed to improve operation conditions during PCI’s, particularly phyisician comfort and safety.
It is a minimally invasive procedure, during which a catheter is inserted into the body at the wrist (radial artery) or the groin (femoral artery). This catheter travels up the peripheral blood vessels to the start of the blocked coronary artery.
A contrast medium may be injected into the catheter to make the progression of the instruments visible on x-ray imaging monitors.
Following this, a guidewire is inserted into the catheter and placed in the blocked artery. It is moved to the lesion by the cardiologist, who is seated at the radioprotected control unit.
Subsequently, a stent-carrying balloon, previously mounted on the guidewire, then moves to the lesion to be treated and is inflated, so that the lumen of the artery (the space inside the vessel) is restored and the blood circulation through this zone is improved.
The balloon is then deflated so the device can be removed, leaving the stent in place.
All these actions are carried out by the cardiologist from the robotic platform’s radioprotected control unit.
- Optimized stent placement
- Safe navigation
- Increased physician comfort
- Reduced stress (protection from x-rays)
In the case of cerebral infarction, the treatment consists of unblocking the obstructed vessel as quickly as possible. Two methods are currently used to do this:
- Thrombolysis (fibrinolysis): this involves an intravenous injection of a drug that can dissolve the blood clot blocking the vessel
- Mechanical thrombectomy: Several recent studies1 have demonstrated the benefits of mechanical thrombectomy. This operation consists of passing a catheter along the artery to the obstructing clot and sucking or ‘catching’ the clot using a stent. This technique enables longer intervention times (up to 6 hours after the stroke) than thrombolysis (limited to 4.5 hours for intra venous perfusion and 6 hours for arterial access with the introduction of a catheter)
1 Mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic strokeL. Derex, T.-H. Cho, 2017
The medical robot R-One has been created for treating coronary artery disease, Robocath has started R&D work with a view to designing a robotic assistance platform for mechanical thrombectomy.
In addition to the benefits of this new treatment, robotic assistance will enable surgeons to carry out procedures under better conditions (complete protection from x-rays, precise navigation, etc.).
- 74% of interventional cardiologists are interested in enhancing their manual movements*
- 63% have concern regarding radiation occupational hazards*
- 97% consider the fact to be perceived as an innovative team center important*
*Independent market study conducted by Suazio in December 2018 on 38 interventional cardiologists (71% in Europe, 26% in US) with a 17 years practice in average (58% are Senior physicians).
- R-Grasp®: this unique, anthropomorphic technology facilitates the navigation of instruments inside the vascular system, making it possible to reproduce hand movements at any point (independent or simultaneous rotation and translation). The right joystick alone enables the guidewire to be navigated into position. The left joystick controls the catheter stent/balloon previously placed on the guide. This intuitive control system allows physicians to easily familiarize themselves with it.
- R-Lock®: Locking the guidewire in the robotic unit ensures that it remains perfectly stable throughout the intervention and that access to the lesion is maintained during the procedure. This system significantly improves interventional conditions.
In addition to its anthropomorphic nature, replicating hand movements identically, R-One™ offers a greater level of freedom of movement than a manual procedure (repeatability, one-handed guidance, etc.). This presents new movement possibilities like continuous rotation (Easy-Loop®).
Comfort and safety for medical staff- Radio-Stop®: thanks to the mobile radioprotection control station, interventional cardiologists can carry out interventions remotely. This means they are protected from x-rays, known to cause recognized occupational diseases such as cancer2. The intervention is carried out in a safe environment, with considerably reduced stress levels for physicians.
- Ergonomic position: procedures are carried out while seated at mobile radioprotection control station.
- Close visualization: visual proximity with radiography screens
2 Brain and neck tumors among physicians performing interventional procedures (2013)
- Open Architecture: R-One™ has a universal architecture, making it compatible with market leading devices1. Its design means it can be adapted to any cath lab. It does not require any specific equipment or technical changes before installation (layout of components, type of flooring, etc.).
- Intuitive control
- Minimal learning curve
- Radial and femoral access
- Easy-Click®: devices introduction into R-One™ only takes a second and the disposable set-up requires only a few minutes before each procedure
- 1 Guidewires and rapid exchange stents/balloons
A stroke can be caused by the obstruction or rupture of a blood vessel supplying the brain. In most cases, a vessel is obstructed. This is called an ischemic stroke. A ruptured vessel is called a hemorrhagic stroke.
A stroke represents an extreme emergency, as it can have severe consequences. Time is a key factor. The quicker a stroke is treated, the lower the risk of serious adverse effects.
