- Home
- Companies
- Invenio Imaging Inc.
- Products
- NIO Laser Imaging System
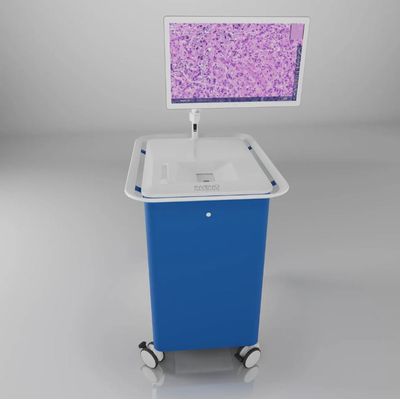
NIO Laser Imaging System
The NIO Laser Imaging System uses Stimulated Raman Histology to image unprocessed tissue specimen without sectioning or staining, enabling histologic evaluation outside the laboratory. It has been used in over 2000 brain tumor procedures across multiple institutions in the United States and in Europe.
The NIO Laser Imaging System is based on Stimulated Raman Histology (SRH), first described by Orringer et al. in 2017 and based on Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy, which was first described by Freudiger et al. in 2008. SRH allows three-dimensional imaging of thick specimens using optical sectioning and relies on laser spectroscopy to interrogate the chemical composition of the sample. As such, it does not require physical sectioning, (e.g. with a microtome on frozen or paraffin-embedded tissue) or dye staining, and it allows optical imaging of fresh tissue specimens with minimal tissue preparation.
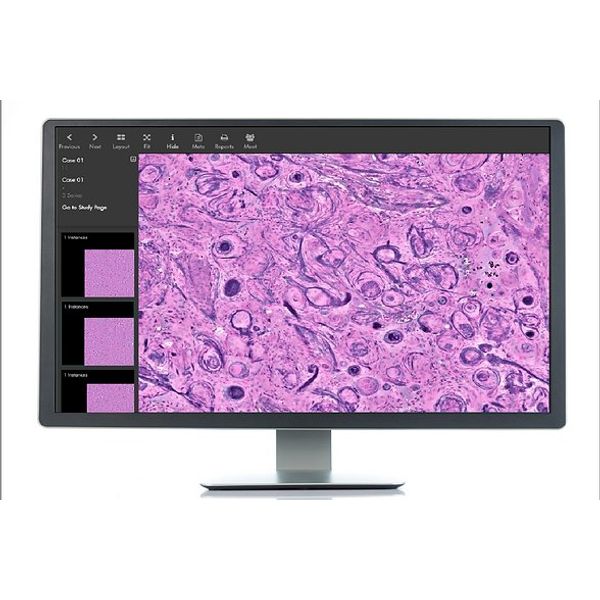
In contrast to other laser spectroscopy techniques, SRH is unique in that it performs a spectroscopic measurement at each pixel and displays the results as a pseudo-color image, instead of a point spectrum. For example, the figure shows how light absorption by CH2 molecular vibrations (e.g. from lipids) and CH3 molecular vibrations (e.g. from proteins and DNA) can be displayed in a pink/purple color scheme. While SRH is not identical to hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) staining, this color scheme has many similarities to traditional stains, such as a high contrast for nuclear features. The NIO Laser Imaging System uses a high numerical aperture objective with 25x magnification and a 0.5mm scan width. Larger areas up to 10mm x 10mm can then be acquired by stitching multiple fields of view in a fully automated process.