- Home
- Companies
- Liberate Medical, LLC
- Products
- VentFree - Respiratory Muscle ...
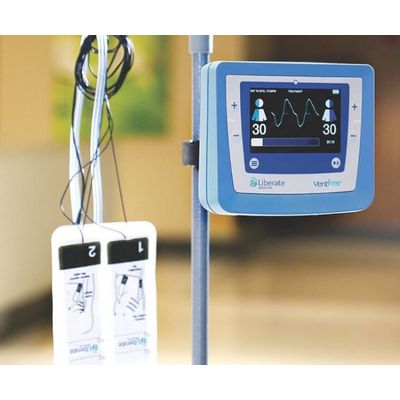

VentFree - Respiratory Muscle Stimulator
Stimulate to Liberate: Preparing to wean from day one of mechanical ventilation.
VentFree contracts the expiratory muscles during mechanical ventilation to keep them active.
In doing so, it may reduce atrophy and may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation.
Expiratory muscles play an important role in respiration, especially in patients with impending respiratory failure.*
Although mechanical ventilation provides life sustaining respiration, prolonged use is associated with negative side effects, including respiratory muscle atrophy.
Expiratory muscle atrophy is found in mechanically ventilated patients and is associated with weaning failure and delayed extubation.*
Patients who require more than four days of mechanical ventilation suffer from high rates of hospital mortality, morbidity and post-discharge complications.*
The VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator uses proprietary non-invasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation.
As electrical stimulation does not require patient cooperation, therapy can begin from day one of mechanical ventilation while patients are sedated or delirious.
This breakthrough approach, which is quick and simple to use, is intended to reduce abdominal muscle atrophy, which may reduce the time taken to liberate patients from mechanical ventilation.
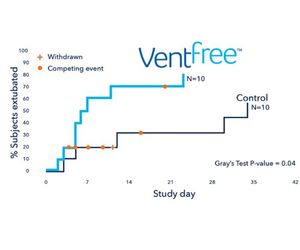
A pilot randomized controlled trial found that mechanical ventilation duration and ICU length of stay were shorter in patients who received stimulation with VentFree muscle stimulator compared to those who received placebo.*
Reduced days on mechanical ventilation can potentially lead to reduced morbidity and mortality, improved quality of life and significant savings for the health care provider.*