

- Home
- Companies
- Solinas Medical, Inc.
- Products
- Solinas ReTAP - Vascular Patch
Solinas ReTAP - Vascular Patch
510(k) cleared device for cardiovascular patching where repeated access is desired. Designed to reduce leakage after cannulation in AV access systems. Constructed of novel composite material. Available in multiple sizes & shapes that conform to vessels. Preclinical testing demonstrates enhanced durability and resistance to leakage.
- More than 600,000 individuals with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) in the U.S. costing the
healthcare system nearly $30 billion per year. 1 - Hemodialysis (HD) is the most common treatment option for patients with ESRD.1
- Most patients on HD rely on a functioning AV fistula or graft to provide permanent blood access. 2
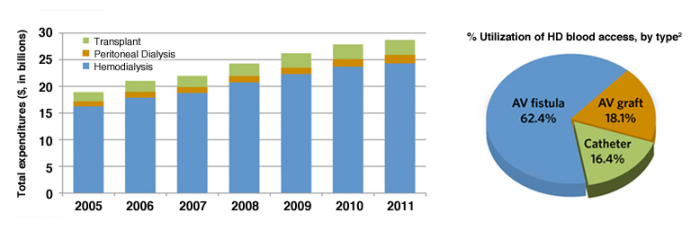
There are several serious complications resulting from frequent, repeated cannulations with large bore (14 to 16 gauge) needles in the hemodialysis setting, including:
Bleeding – caused by venous needle and access site clot dislodgement.
Pseudoaneurysms – results from hemodynamic loading and vessel wall degradation due to >300 cannulations per year.
Thrombosis – partly due to disruption or cessation of blood flow resulting from prolonged compression applied to achieve post-dialysis hemostasis.
Maintaining an adequate and functioning vascular access is critical to providing efficient hemodialysis treatments for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. While ESRD patients comprise only slightly more than 1% of the total Medicare population, total Medicare expenditures of $28.6 billion in 2012 for these individuals patients represented 5.6% of total Medicare costs. A significant percentage of these costs are associated with the creation and maintenance of hemodialysis access with many patients often requiring multiple interventions to treat clotted and failing AV fistulas and grafts. According to the United States Renal Data System (USRDS) Medicare annual spending per patient in 2011 for hemodialysis patients with a failing AV graft was $112,333 compared to only $24,438 for patients with a functional hemodialysis graft. Identifying options for decreasing vascular access related complications would lead to improved clinical outcomes while also decreases costs to the healthcare system.
Handling
Peel open the sterile pouch and carefully remove the patch using sterile, atraumatic instruments or gloves. It is not necessary to pre-clot the ReTAP™ Patch.
Sizing
The ReTAP™ Patch is intended for peripheral vascular patching for vessels that are approximately 6 to 10 mm in diameter and where a curved patch is desired. Do not form a larger patch by suturing separate patches together since doing so may result in an inadequate implantation result.
Suturing
It is recommended only non-absorbable, monofilament, suture with a non-cutting, tapered, needle of appropriate size be used. Use a minimum 2 mm suture bite in cardiac and great vessel applications. For peripheral applications, use a minimum 1 mm suture bite. Use appropriate suture size and placement to prevent gaps. Use minimal tension when pulling up on the suture line or when placing a knot. This will minimize suture line bleeding. Use the smallest needle that is appropriate for the procedure.
Contraindications
The ReTAP™ Cardiovascular Patch is not indicated for:
- Reconstruction of hernias and tissue deficiencies.
- Reconstruction and repair of passive biological membranes such as duramater, pericardium, or peritoneum.
Use of this product in non-cardiovascular applications can potentially cause complications, for example: failure of closure or repair, suture pull out, or undesired healing to surrounding tissues.
Precautions
- Do not use absorbable sutures.
- Do not use a cutting needle.
- Do not use less than a 2 mm suture bite in all cardiac and great vessel applications.
- Do not use less than a 1 mm suture bite in all peripheral applications.
- Do not contaminate or damage the patch.
- Suture line bleeding may occur if suture holes are elongated, torn, or if large gaps are allowed to form between the prosthetic material and the native tissue.
- Only qualified physicians in cardiovascular surgery techniques should use the prosthesis.
- The healthcare provider is responsible for all appropriate postoperative care instructions to the patient.
- Aseptic technique should be used for all cannulation procedures.
- Fistula should be mature, ready for cannulation with minimal risk for infiltration, and able to deliver the prescribed blood flow throughout the dialysis procedure.
- Ensure needle cannulations of the ReTAP™ patch are evenly spaced along the length of the patch when used for vascular access and when repeated needle punctures may be necessary.
- Mechanical damage to the patch may result from repeated needle cannulations, which could lead to hematoma or pseudoaneurysm formation.
- Patients should be carefully monitored during and immediately following the dialysis procedure.
