Drug Solubility Articles & Analysis: Older
21 articles found
When studied in living organisms, this relationship is referred to as in vivo PK/PD, a discipline that provides invaluable insights into drug behavior within a biological context. Pharmacokinetics: The Journey of a Drug The pharmacokinetic profile of a drug describes its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes. ...
Ensuring the stability and bioavailability of the drug substance in a liquid environment remains a cornerstone of formulation science, demanding specific expertise and technological know-how. ...
Glycosylated impurities refer to a kind of glycosylated product formed during the synthesis, storage, and use of drugs, mainly resulting from non-enzymatic reactions between sugars and drug molecules. ...
The unique properties of PEG derivatives, including their biocompatibility and ability to modify the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of drugs, make them indispensable in modern pharmacology. This article explores the diverse applications of PEG derivatives in pharmaceuticals and drug delivery, shedding light on how they are shaping the ...
Introduction In the ever-evolving landscape of drug delivery systems, nanoformulation stands out as a revolutionary approach. ...
Applications of PEGs and Carboxylic Acid PEGs Drug Delivery PEG and its carboxylic acid derivatives have important applications in drug delivery. PEG-modified nanoparticles can enhance drug bioavailability and targeting by increasing particle stability, improving drug solubility, and reducing recognition by the ...
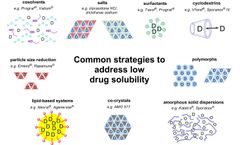
The physical and chemical properties of drug molecules such as solubility, stability and bioavailability can be improved through salts/co-crystals. Process of Polymorph Screening and Selection When drug molecules crystallize in different crystal forms, their bioavailability, solubility, dissolution rate, chemical and physical ...
In this article, we will explore different types of nanoparticle development that are revolutionizing drug delivery systems. Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Polymer nanoparticles are a popular choice for drug delivery systems due to their biocompatibility and versatility. ...
Conventional liposomes As a drug delivery system, traditional liposomes can change the pharmacokinetic properties and tissue distribution of tumor drugs, enhance the target aggregation concentration of drugs, and enhance drug efficacy. ...
Biopharma PEG, a leading innovator in polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives, proudly introduces its featured Azide PEG series, which can be used in drug development, click chemistry, ADCs (Antibody Drug Conjugates), PROTACs (Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras), and beyond. ...
These characteristics enable better drug spreading over the skin, resulting in enhanced drug absorption. ...
Coated Microneedles Coated microneedles are also known as surface drug-loaded microneedles. The drug is attached to the surface of the microneedle by infiltration, coating or drug loading outside the needle. ...
The drug layer is typically applied by spraying a drug solution or drug suspension onto the surface of the tablet, depending on drug solubility and dosage. ...
Morphological parameters did not affect the encapsulation efficiency. Using passive drug loading methods, water-soluble drugs are encapsulated within the aqueous phase of the liposome, while lipid-soluble drugs are encapsulated in the lipid phase of the liposome. The lipid-soluble portion of the ...
The characteristics of liposomes make cosmetics have the following characteristics: Multiple power Liposomes are amphiphilic and act as carriers that can bind a variety of soluble nutrients, such as water-soluble vitamin C and oil-soluble vitamin E. In addition, there are also many studies on composite liposomes, which can combine ...
Research Scope on Drug Stability Analysis Chemical stability refers to changes in drug content (or potency) due to chemical reactions such as hydrolysis and oxidation. ...
Pharmaceutical excipients are substances formulated together with active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) of the drug, and excipients account for most of the drug composition. Excipients are designed to interact with and enhance the properties of APIs. ...
Pharmaceutical excipients are natural or synthetic substances formulated together with the active ingredients of the drug, whose purpose is to increase the formulations containing effective active ingredients or endow the active ingredients in the final dosage form with therapeutic effects, such as promoting drug absorption or solubility. ...
For example, AstraZeneca's Accolate® (Zalukast) tablets contain amorphous API and are stable during production and storage. For drugs with low solubility, an amorphous solid dispersion can be considered. Since the energy required for amorphous dissolution is low, it is beneficial to increase the solubility without reducing the permeability of ...
In the process of preparing drugs into liquid preparations, a common problem is that most drugs are poorly soluble in water. ...